Automation with JUnit
Test reference in Squash TM
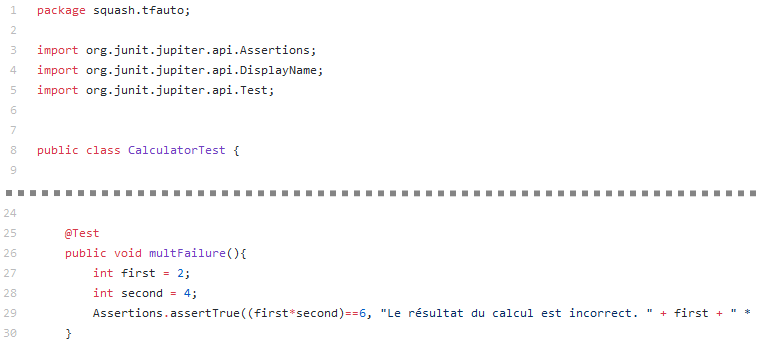
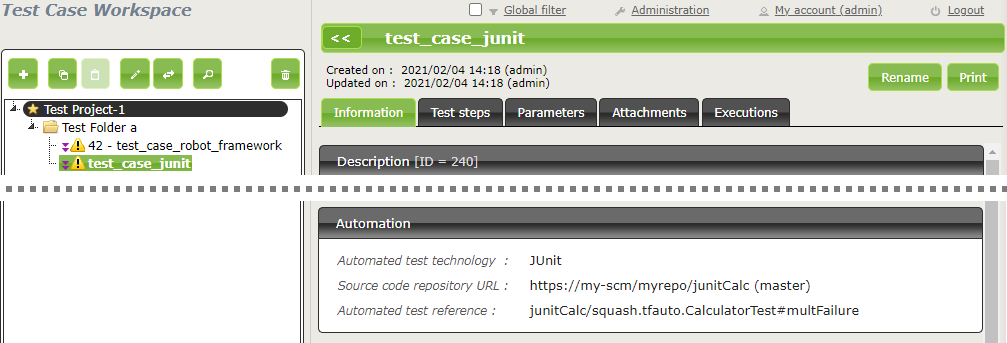
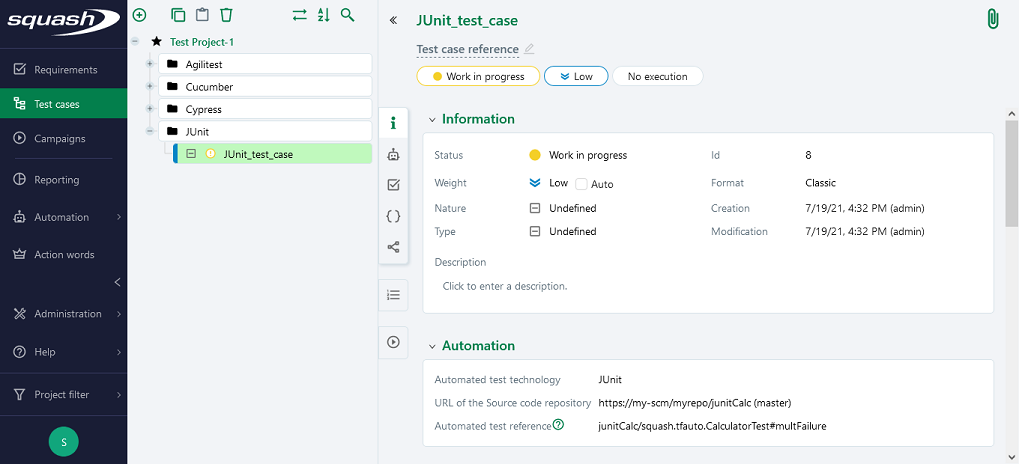
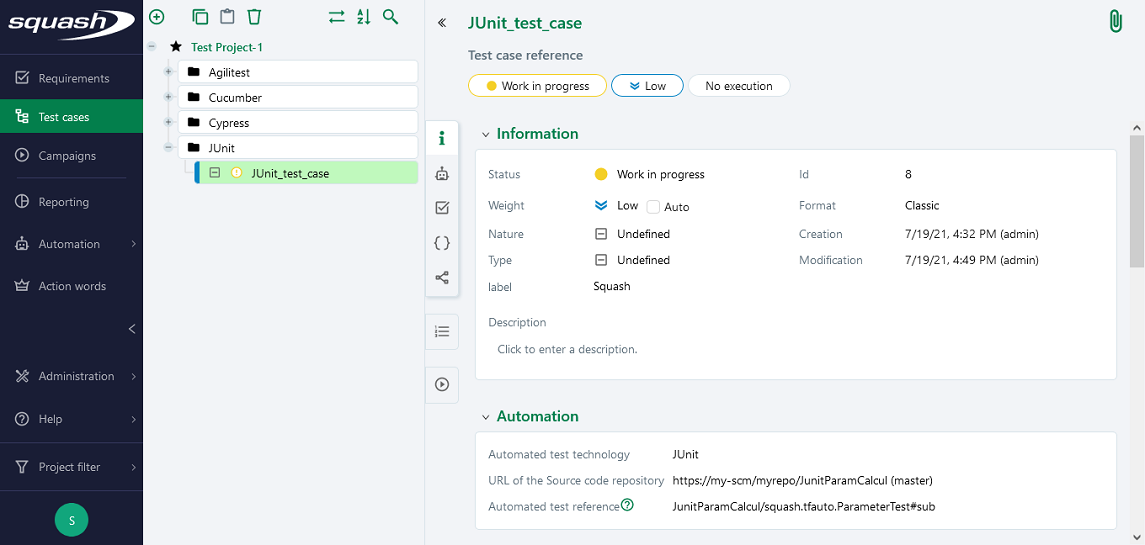
In order to bind a Squash TM test case to a JUnit automated test, the content of the Automated test reference field of the Automation block of a test case must have the following format:
[1] / [2] # [3]
With:
-
[1]: Name of the project on the source code repository. -
[2]: Qualified name of the test class. -
[3]: Name of the method to test in the test class. This parameter is optional.
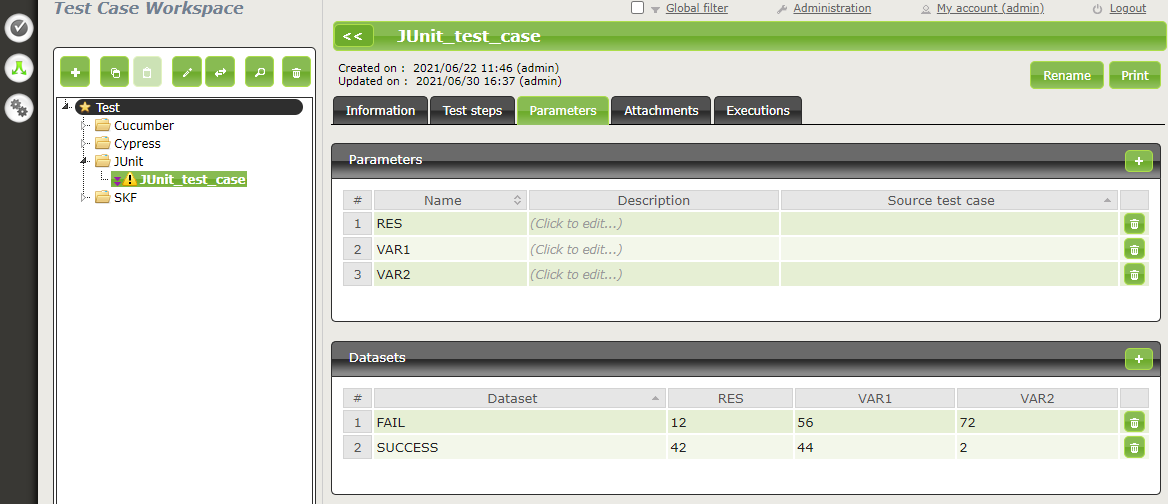
Below is an example of a test class and the corresponding Squash TM test case automation:

Nature of the exploitable Squash TM parameters
The exploitable Squash TM parameters in a JUnit script will differ depending on whether you're using the Community or Premium version of Squash DEVOPS.
Here is a table showing the exploitable parameters:
| Nature | Key | Community | Premium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name of the dataset | DSNAME | ✅ | ✅ |
| Dataset parameter | DS_[name] | ✅ | ✅ |
| Test case reference | TC_REF | ✅ | ✅ |
| Test case custom field | TC_CUF_[code] | ✅ | ✅ |
| Iteration custom field | IT_CUF_[code] | ❌ | ✅ |
| Campaign custom field | CPG_CUF_[code] | ❌ | ✅ |
| Test suite custom field | TS_CUF_[code] | ❌ | ✅ |
Legend:
[code]: Value of the "Code" of a custom field[name]: Parameter name as filled in Squash TM
Squash TM parameters usage
It is possible when running an automated Squash TM test case with JUnit to exploit Squash TM parameters within it.
To do this, the following steps must be followed:
-
Fill in custom fields in Squash TM and associate them with the project containing the test plan to be executed.
-
Import opentestfactory-java-param-library into the JUnit project containing the tests to run by adding to the
pom.xmlfile:- the following Maven repository:
<repositories> <repository> <id>org.squashtest.repo.release</id> <name>Squashtest repository for releases</name> <url>https://repo.squashtest.org/maven2/release</url> </repository> </repositories>- the following Maven dependency:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.opentestfactory.util</groupId> <artifactId>opentestfactory-java-param-library</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> -
You can then retrieve the value of a Squash TM parameter of the desired type using the following syntax:
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getString("paramName");
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getInt("paramName");
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getFloat("paramName");
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getDouble("paramName");
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getBoolean("paramName");
-
The above methods look for the desired parameter in the test parameters transmitted by Squash TM; if they cannot find it, they then look for it in the global parameters transmitted by Squash TM.
These methods throw aParameterNotFoundExceptionif the parameter is not found. If the parameter is found but cannot be converted to the desired type, aParameterFormatExceptionis thrown. Consider handling these exceptions in your test classes.
Warning: the conversion of Boolean data returnstruewhen the character string to be converted is equal to"true"(whatever the case),falsein all other cases; but never propagates an exception. -
It is also possible to define a default parameter in the case where the Squash TM parameter is non-existent by using the following syntax:
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getString("paramName", defaultValue);
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getInt("paramName", defaultValue);
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getFloat("paramName", defaultValue);
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getDouble("paramName", defaultValue);
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getBoolean("paramName", defaultValue);
-
The above methods therefore do not propagate a
ParameterNotFoundExceptionwhen the Squash TM parameter sought is not found but propagate aParameterFormatExceptionif the Squash TM parameter is found, but cannot be converted to the desired type. -
It is also possible to target a test parameter or a global parameter with specific methods. As with the previous methods, they are available in versions with and without default parameters. Here are a few examples:
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getTestString("paramName");
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getGlobalInt("paramName");
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getTestFloat("paramName", defaultValue);
ParameterService.INSTANCE.getGlobalBoolean("paramName", defaultValue);
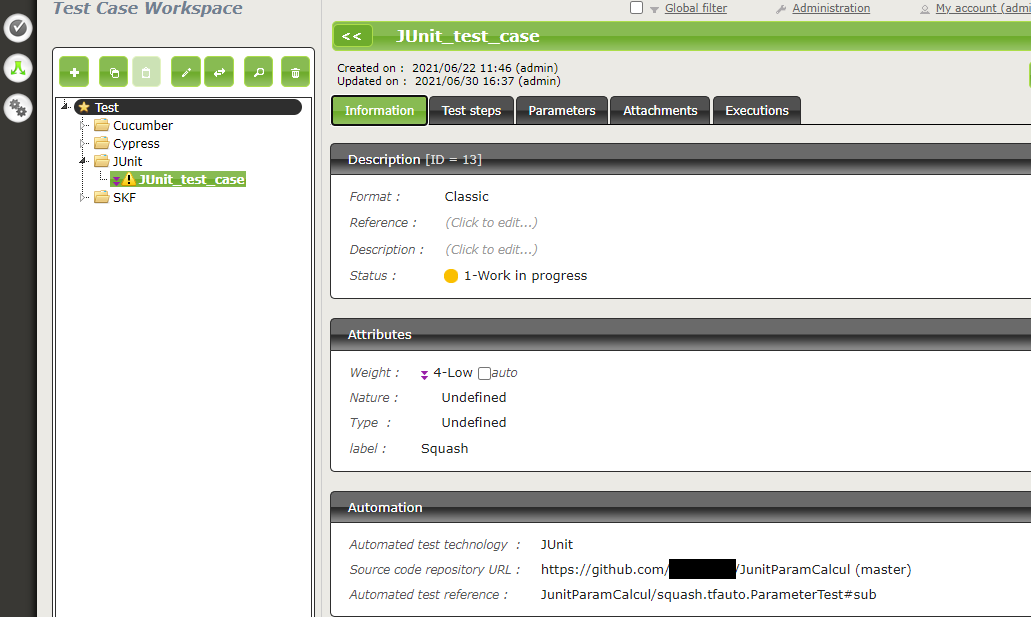
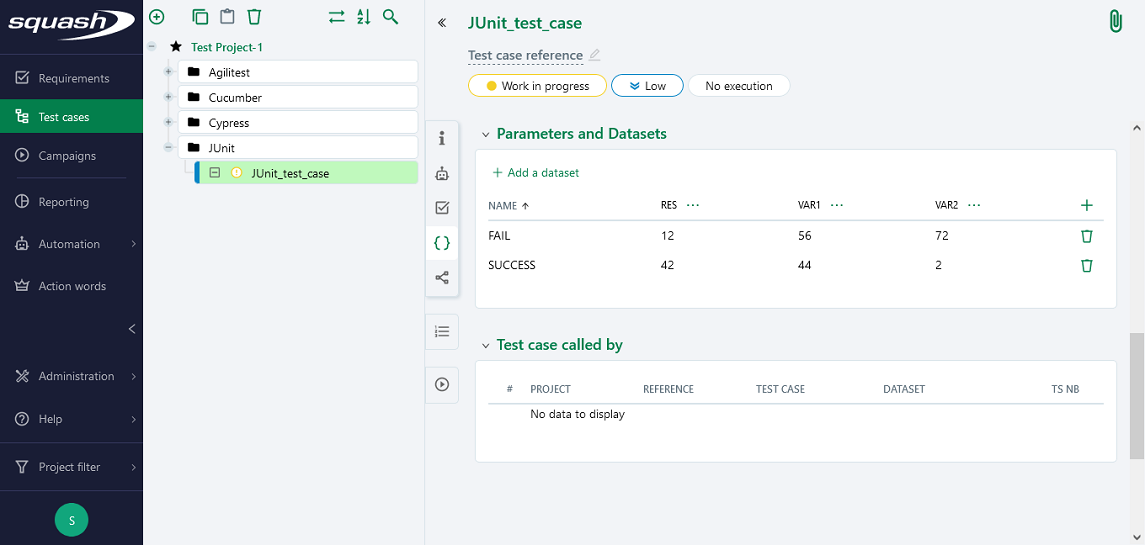
Below is an example of a JUnit test file and the automation of the associated Squash TM test case:


Supported versions
Squash AUTOM and Squash DEVOPS have been validated with
- JUnit 4.12, any JUnit 4 version more recent should work properly
- JUnit 5.3.2, any JUnit 5 version should work properly
Additionally, it is advised to use Surefire 2.19.1 or later.