Automation with Robot Framework
Configuration of the test environment
The allure-robotframework Python module must be present in the test environment.
It can be installed with the command:
pip install allure-robotframework
In order to retrieve the Squash TM parameters, the squash-tf-services Python library must be present.
It can be installed with the command:
pip install squash-tf-services
Test reference in Squash TM
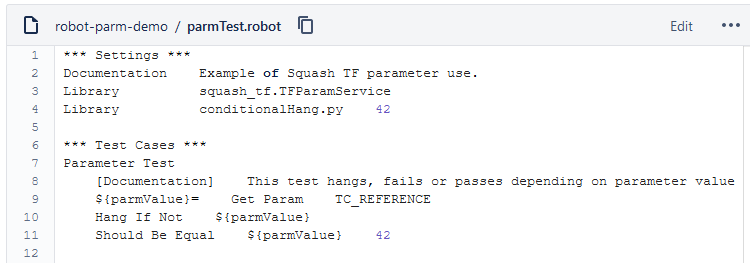
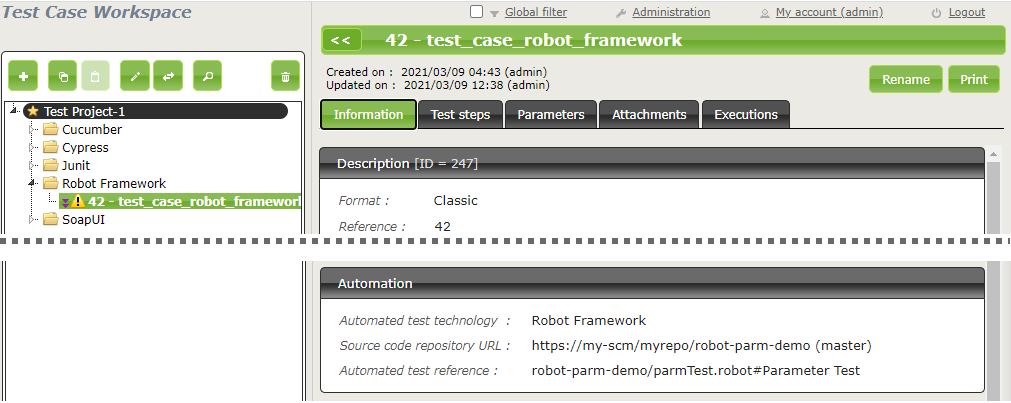
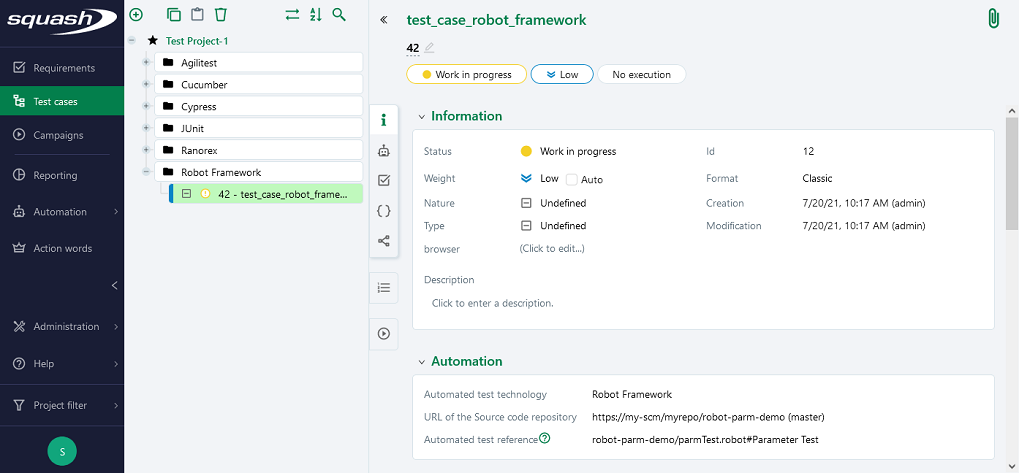
In order to bind a Squash TM test case to a Robot Framework automated test, the content of the Automated test reference field of the Automation block of a test case must have the following format:
[1] / [2] # [3]
With:
[1]: Name of the project on the source code repository.[2]: Path and name of the Robot Framework test, from the root of the project (with the.robotextension).
It is possible to not indicate a.robotfile name and, instead, only define the name of a folder. In this case, all the.robotfiles of this folder and its sub-folders will be executed.[3]: Name of the test case to execute in the.robotfile(s). This parameter is optional.
Nature of the exploitable Squash TM parameters
The exploitable Squash TM parameters in a Robot Framework script will differ depending on whether you're using the Community or Premium version of Squash DEVOPS.
Here is a table showing the exploitable parameters (these parameters are transmitted as test parameters, see below, Squash TM does not generate global parameters):
| Nature | Key | Community | Premium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name of the dataset | DSNAME | ✅ | ✅ |
| Dataset parameter | DS_[name] | ✅ | ✅ |
| Test case reference | TC_REFERENCE | ✅ | ✅ |
| Test case custom field | TC_CUF_[code] | ✅ | ✅ |
| Iteration custom field | IT_CUF_[code] | ❌ | ✅ |
| Campaign custom field | CPG_CUF_[code] | ❌ | ✅ |
| Test suite custom field | TS_CUF_[code] | ❌ | ✅ |
Legend:
[code]: Value of the "Code" of a custom field[name]: Parameter name as filled in Squash TM
As indicated, Squash TM adds a prefix to the code of the transmitted custom field. Make sure to take it into account.
Refer to the Squash TM documentation for more information about custom fields.
Parameters usage
It is possible, when running Robot Framework tests, to exploit parameters within it. A parameter can be a test parameter or a global parameter. Squash TM transmits only test parameters. Test parameters and global parameters can be used in Squash DevOps with the robotframework/params action.
In order to achieve this, you have to follow these steps:
-
Import the squash-tf-services library in the
Settingssection of the.robotfile:Library squash_tf.TFParamService -
You can then retrieve the value of a parameter by calling one of the following keywords:
-
This keyword retrieves the value of a global parameter.${value}= Get Global Param key ${value}= Get Global Param key default_value
If it exists, its value is assigned to${value}.
Otherwise the default value is assigned to${value}; if no default value was provided,Noneis used.
Example:${parameter}= Get Global Param target_base_url http:localhost:8080/sut/ -
This keyword retrieves the value of a test parameter.${value}= Get Test Param key ${value}= Get Test Param key default_value
If it exists, its value is assigned to${value}.
Otherwise the default value is assigned to${value}; if no default value was provided,Noneis used.
Example:${login}= Get Test Param TC_login test_user -
This keyword combines both types of parameters.${value}= Get Test key ${value}= Get Test key default_value
If a test parameter exists, its value is assigned to${value}.
Otherwise, if a global parameter exists, its value is assigned to${value}.
Otherwise, the default value is assigned to${value}; if no default value was provided,Noneis used.
Example:${login}= Get Param login test_user
-
Example
Below is an example of a Robot Framework test file and the corresponding Squash TM test case automation:

Supported versions
Squash AUTOM and Squash DEVOPS have been validated with Robot Framework 4.0. Any recent version should work properly.